How Shipping Zones Affect Fulfillment Costs
Shipping zones are a critical factor in determining how much it costs to ship orders. Carriers like USPS, UPS, and FedEx calculate these zones based on the distance between your warehouse and the customer’s location. The farther the package travels, the higher the zone - and the higher the cost. For example, shipping a 5-pound package from Zone 2 to Zone 8 can increase costs by 74–90%.
Here’s the takeaway:
- Shipping costs rise significantly with distance. A USPS Priority Mail package costs about $9.35 in Zone 2 but jumps to $17.75 in Zone 8.
- Hidden fees add up. Fuel surcharges, residential delivery fees, and peak season surcharges can further inflate costs.
- Customer expectations are high. 90% of shoppers expect delivery in 2–3 days, and 70% abandon carts if shipping costs are too high.
To reduce these costs, businesses can use strategies like placing inventory in multiple fulfillment centers, zone skipping (bulk shipping to reduce zone distances), and using tools like Navexa to compare carrier rates. By optimizing shipping zones, you can cut costs by 40–60% and improve delivery times.
Key Insight: Analyze your customer locations and adjust your fulfillment strategy to keep shipments in lower-cost zones. It’s one of the most effective ways to save money and meet delivery expectations.
Optimizing Your Shipping Costs: 5 Factors You Must Know
What Are Shipping Zones?
Shipping zones are a way to group ZIP codes to measure the distance between your warehouse and your customer’s location. Carriers like USPS, UPS, and FedEx use the first three digits of both the origin and destination ZIP codes - not the actual road mileage - to determine the zone.
Your warehouse is considered Zone 1, and zones increase as the distance from your location grows. For domestic U.S. shipments, zones typically range from Zone 1 (closest, covering 0–50 miles) to Zone 8 (farthest, covering 1,801+ miles). Zone 9 is reserved for U.S. territories such as Guam and American Samoa.
Here’s something to keep in mind: ZIP code boundaries can create unexpected zone differences. For example, two customers just 10 miles apart might fall into different zones. Because of this, you can’t rely on a map to estimate zones accurately. Instead, you’ll need to consult carrier-specific zone charts or use their online zone calculators.
How Carriers Calculate Shipping Zones
Carriers calculate zones by matching the first three digits of your warehouse’s ZIP code with the first three digits of your customer’s ZIP code. Each carrier provides zone charts that map these ZIP code pairs to specific zones, and you can find these charts on their websites or through online tools.
Shipping zones directly affect your shipping costs. For instance, a 5-pound USPS Priority Mail package costs about 90% more to ship to Zone 8 than to Zone 2. Similarly, UPS Ground rates jump by 83% for the same zone difference. These costs are influenced by either the actual weight or the dimensional weight (calculated as length × width × height ÷ divisor). This means that larger, lightweight packages can face even higher fees due to zone-based pricing.
Zone Differences Between Carriers
While all major carriers use zones, their definitions and numbering systems vary. USPS uses Zones 1–9, with Zone 9 covering U.S. territories. UPS and FedEx Ground, on the other hand, typically use Zones 2–8 for shipments within the continental U.S. and assign special codes for non-continental areas. For example, UPS designates Zone 44 for Metro Alaska and Hawaii, Zone 45 for Puerto Rico, and Zone 46 for remote parts of Alaska and Hawaii.
The type of service you choose can also affect zone numbering. FedEx Ground uses eight zones, but FedEx Priority Overnight may have up to 16 zones. Similarly, UPS Next Day Air and UPS 3 Day Select use higher zone numbers. However, not all services are zoned. USPS First-Class Mail and Media Mail, for instance, charge flat rates regardless of distance, making them a cost-effective option for lightweight items traveling long distances.
Understanding these variations is key to managing your shipping costs effectively and ensuring your fulfillment strategy stays on track.
How Shipping Zones Affect Your Costs
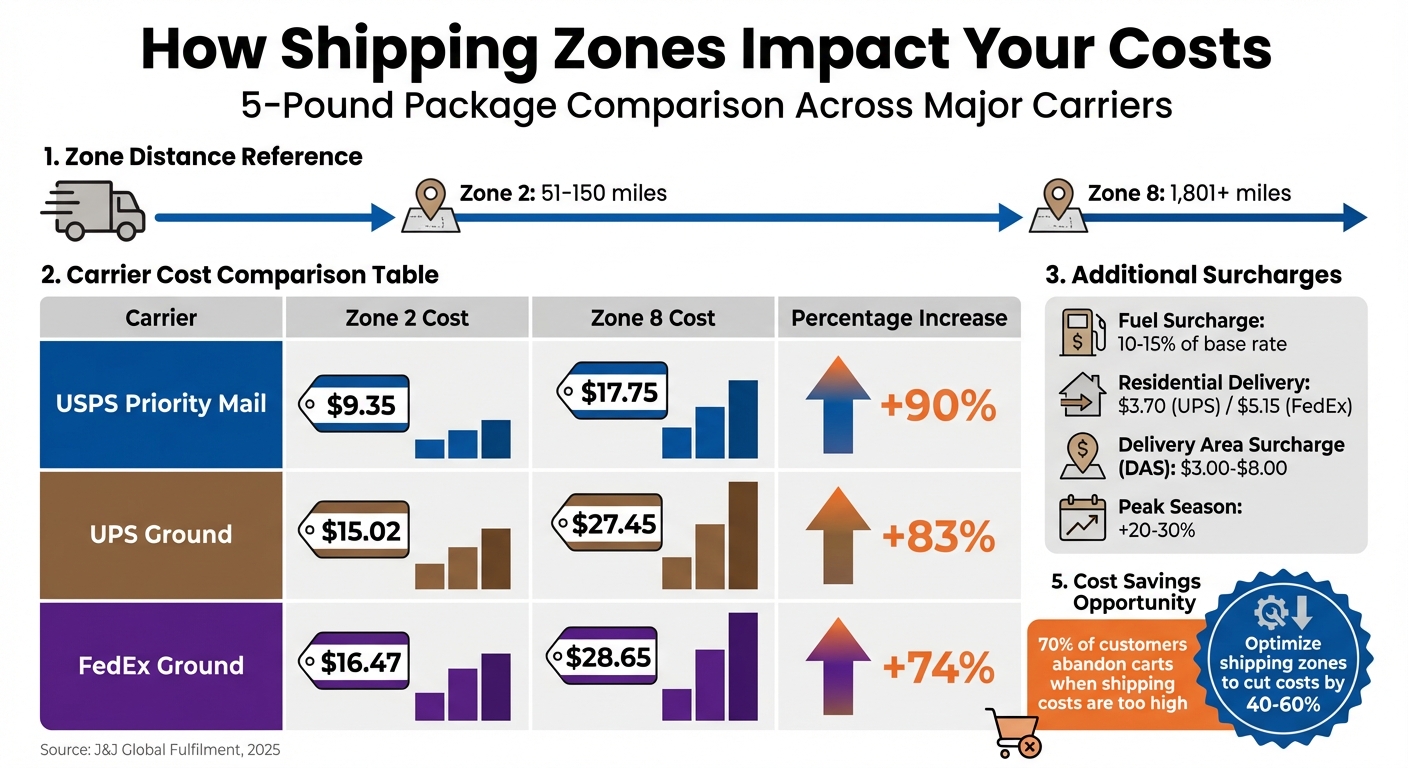
Shipping Zone Cost Comparison: USPS, UPS, and FedEx Rates by Distance
Shipping zones play a key role in determining your shipping costs. The concept is simple: the farther a package needs to travel, the higher the cost. This increase reflects factors like higher fuel expenses, longer transit times, and more complex logistics.
The price difference between zones can be striking. Take a 5-pound package shipped via USPS Priority Mail: sending it to Zone 2 (within 150 miles) costs about $9.35, but shipping the same package to Zone 8 (1,801+ miles) jumps to roughly $17.75 - a 90% increase. UPS Ground follows a similar trend, with costs rising from approximately $15.02 in Zone 2 to $27.45 in Zone 8, which is an 83% increase.
"Weight and zones work together to create shipping cost scenarios that can shock businesses. We've seen companies discover they're losing money on every order to certain states simply because they never calculated the true landed cost including zone-based shipping."
– Neil Sant, Chief Operations Officer, J&J Global Fulfilment
Base Shipping Rates by Zone
As zones increase, so do base rates, and the gap grows even wider for heavier packages. For example, shipping a 1-pound package with USPS Priority Mail costs $9.60 in Zone 2 and $14.25 in Zone 8 - a difference of $4.65. But for a 3-pound package, that gap expands to $12.25, with rates climbing from $11.70 to $23.95.
Here’s a snapshot of how major carriers compare for a 5-pound package:
| Carrier | Zone 2 Cost | Zone 8 Cost | Percentage Increase |
|---|---|---|---|
| USPS Priority Mail | ~$9.35 | ~$17.75 | ~90% |
| UPS Ground | ~$15.02 | ~$27.45 | ~83% |
| FedEx Ground | ~$16.47 | ~$28.65 | ~74% |
Source: J&J Global Fulfilment, 2025
Amazon Shipping rates, updated as of January 6, 2026, show a similar trend. A 10-pound package costs $15.85 in Zone 2 but increases to $26.38 in Zone 8 - a 66% jump. Even lighter packages feel the pinch: a 1-pound shipment rises from $11.99 in Zone 2 to $15.01 in Zone 8.
These differences in base rates emphasize why having a strategic fulfillment plan is essential. And it’s not just the base rates - additional fees for distant zones can significantly raise overall costs.
Extra Fees That Increase with Zones
On top of base rates, additional surcharges can make shipping to farther zones even more expensive. If these fees go unnoticed, they can cut into your profits.
- Fuel surcharges typically add 10% to 15% of the base rate. Since base rates are higher for distant zones, these surcharges grow as well. For example, a $10 shipment in Zone 2 might incur a $1.50 fuel fee, while an $18 shipment in Zone 8 could add $2.70.
- Residential delivery fees tack on about $3.70 per package for UPS and $5.15 for FedEx.
- Delivery Area Surcharges (DAS) apply to remote or rural locations, ranging from $3.00 to $8.00 per package. A $20 base rate combined with these surcharges could push the total cost above $30.
- Peak season surcharges during Q4 can add another 20% to 30% to your shipping costs.
- Dimensional weight pricing increases costs for bulky but lightweight items, as the calculated weight is multiplied by the higher zone rate.
Understanding these layered costs is critical. Studies show that about 70% of customers abandon their carts when shipping fees seem too high. Whether you’re absorbing these costs or passing them on to customers, they can impact both your profits and your sales. Managing these expenses effectively is key to staying competitive.
sbb-itb-ed0a9d1
How to Reduce Zone-Based Shipping Costs
Looking to cut down on zone-based shipping expenses? Here are some strategies that can make a real difference.
Zone Skipping
Zone skipping simplifies the process by consolidating multiple orders heading to the same destination into a single freight shipment. Instead of sending each package individually through multiple zones, the consolidated shipment is sent directly to a carrier hub in the destination zone. From there, packages are handed off for local delivery, typically at lower Zone 1 or Zone 2 rates.
This approach not only saves money but also reduces the chances of damage or delays since fewer handling points are involved. For example, shipping 1,000 packages from New York to California might cost $20,000 (about $20 per package) if sent individually. With zone skipping, you could spend around $8,000 for bulk freight and $7,000 for last-mile delivery, totaling $15,000 - saving $5,000. To make the most of this method, analyze your order history to identify customer "hotspots" where consolidating shipments makes sense. Keep in mind that last-mile delivery alone can make up about 53% of total shipping costs.
Using Multiple Fulfillment Centers
Spreading inventory across multiple fulfillment centers can significantly cut down on shipping distances and costs. In fact, this strategy can reduce fulfillment expenses by an average of $2 per order and lead to overall savings of about 13%.
With 90% of consumers expecting deliveries within two to three days, having strategically located warehouses is more important than ever. For instance, relying on a single East Coast warehouse to ship to the West Coast (Zone 8) could take 5–7 business days. Adding a West Coast hub could shift those shipments into Zone 2 or 3, enabling faster delivery within 1–2 days. Strategic locations like Tennessee or Utah can help you reach up to 96% of U.S. addresses within two days using ground services.
Choosing the Right Warehouse Locations
Picking the right locations for your warehouses is a game-changer for reducing zone-based shipping costs. By analyzing customer ZIP code data, many businesses find they can serve about 85% of their customers from just two strategically placed facilities instead of maintaining a nationwide network. Most orders typically go to just three or four zones, so focusing on high-demand regions is key.
For example, a bi-coastal strategy or a tri-regional approach - adding a central hub in Texas or Ohio - can shift most customers into Zones 2–4. Using fulfillment centers in California, Texas, and Pennsylvania can eliminate the need to ship from the costliest zones (Zones 7 and 8) for most orders in the continental U.S.. A great case in point is Whites Beaconsfield, which used an Ohio warehouse during a surge in demand sparked by a viral TikTok video. This move significantly cut shipping costs and sped up delivery times by six months compared to their original plan.
Using Navexa for Rate Comparison
Shipping zones vary between carriers, which can make rate comparisons a headache. Manually checking rates for USPS, UPS, and FedEx is not only time-consuming but also prone to errors.
Navexa simplifies this process with its multi-carrier rate shopping tool. It automatically compares real-time rates from major carriers for each zone and service level. By accounting for different zone classifications and surcharges, Navexa helps businesses find the most cost-effective option, often reducing shipping costs by 10–15%.
How Zones Affect Delivery Times and Customer Satisfaction
Shipping zones play a major role in determining how quickly packages arrive and how likely customers are to make repeat purchases. This connection is crucial for maintaining customer loyalty in today's fast-paced market.
Delivery Times by Zone
The farther a package has to travel, the longer it takes to get there - it's that simple. For example, shipments within nearby zones (1–2) typically arrive in 1 to 3 days, while those heading to the farthest zones (7–8) can take 5 to 8 days. This delay happens because packages must pass through more handling steps as they cross the country.
| Zone | Typical Ground Transit Range |
|---|---|
| Zone 1–2 | 1 to 3 days |
| Zone 3 | 2 to 4 days |
| Zone 4 | 3 to 5 days |
| Zone 5 | 4 to 6 days |
| Zone 6 | 5 to 7 days |
| Zone 7–8 | 5 to 8 days |
Here’s the kicker: 90% of consumers expect their orders to arrive within two or three days. Back in 2012, people were okay waiting up to 5.5 days, but now that tolerance has shrunk to just 4.1 days. If a fulfillment center is located far away, slower deliveries are inevitable. In fact, 24% of customers cancel their orders because of slow shipping, and 73% of shoppers now expect deliveries to be both fast and affordable.
Take Karta Bottle as an example. In May 2025, Pete Anwyll, the company’s owner, boosted its US market share from 5% to 55% by teaming up with J&J Global Fulfilment. By spreading inventory across Columbus, Las Vegas, and Toronto, Karta Bottle slashed shipping zones and transit times, making their delivery speeds comparable to domestic US brands. Similarly, Whites Beaconsfield faced a viral TikTok-driven demand surge and adapted by using an Ohio-based fulfillment center. COO James Pryor shifted from shipping out of the UK to a local US fulfillment strategy, which sped up their US expansion by six months and significantly reduced delivery times for American customers.
Next, let’s see how these delivery timelines influence customer expectations during the checkout process.
Providing Accurate Delivery Estimates
Setting clear delivery expectations can go a long way in keeping customers happy and reducing cart abandonment. Instead of offering a vague "3–5 days" estimate for everyone, consider using real-time analytics to display delivery dates tailored to each shipping zone. For instance, a customer in Zone 1 might see "2 days", while someone in Zone 8 would see "6 days".
Navexa’s real-time analytics tools make this possible by factoring in variables like shipping zones, carrier performance, and current inventory locations. This level of precision matters because 70% of customers abandon their carts due to high shipping costs or uncertainty about delivery times. By providing accurate, zone-specific delivery estimates, you not only set realistic expectations but also minimize the chances of customer disappointment or canceled orders.
Conclusion
This guide has explored how shipping zones directly impact both costs and delivery times. With nearly 90% of U.S. consumers expecting their orders within two to three days, navigating these zones effectively is crucial.
The good news? You have the power to manage these costs. By distributing inventory across strategically located fulfillment centers, you can cut shipping expenses and speed up delivery. Techniques like zone skipping, using appropriately sized packaging, and adopting a multi-carrier approach can save up to $2 per order - boosting your bottom line by about 13%.
Tools such as Navexa make implementing these strategies easier. They offer features like automated carrier rate comparisons, optimized packaging solutions, and order routing to the nearest fulfillment center. With real-time analytics and multi-carrier rate shopping, you could reduce shipping costs by 10–15%, all while improving delivery speeds and customer satisfaction.
Take a closer look at your order history and fulfillment setup to identify areas for improvement. Streamlining your shipping strategy not only saves money but also enhances the customer experience. Start optimizing today for a more efficient and customer-friendly operation.
FAQs
How can businesses lower shipping costs for distant zones?
Businesses looking to cut costs on higher shipping zones can benefit from fine-tuning their fulfillment strategies. A smart move is placing inventory closer to customers by utilizing regional fulfillment centers. This reduces the distance packages need to travel, often shifting shipments from higher zones (like Zones 5–8) to lower ones (Zones 1–3), where carrier rates are typically more affordable.
For companies that don’t have the resources to manage multiple warehouses, using a platform that automates multi-carrier rate shopping can be a game-changer. On top of that, intelligent box optimization ensures packaging is as compact as possible, helping to avoid hefty dimensional weight fees. Forecasting regional demand can also play a key role, allowing businesses to position stock strategically and avoid expensive long-haul shipments.
Navexa provides the tools to make these strategies easier. With real-time analytics to pinpoint cost drivers, automated workflows to route orders to the nearest hub, and built-in features for packaging optimization and carrier selection, Navexa helps e-commerce brands lower shipping expenses while keeping operations running smoothly.
How can I improve delivery times and customer satisfaction for distant shipping zones?
To improve delivery times and keep customers happy in far-off areas, start by placing inventory closer to your customers. Using regional fulfillment centers or third-party logistics (3PL) warehouses can shrink the distance packages need to travel, cutting both costs and shipping times. Combine this with smart carrier selection by comparing rates across multiple carriers to find the fastest and most affordable option for each region.
Another important step is streamlining your packaging. Smaller and lighter packages often fall into lower shipping cost brackets, even for long-distance deliveries. Alongside this, inventory forecasting can help you stock popular products in locations with high demand, avoiding the need for costly, last-minute cross-country shipments. You can also speed things up by using order consolidation, bundling multiple items for the same customer into a single shipment to reduce processing time.
Operational upgrades make a big difference, too. For example, automated workflows can direct orders to the nearest fulfillment center based on ZIP codes, while real-time tracking helps you keep tabs on shipments and address delays before they become issues. Providing customers with clear updates, like expected delivery times, builds trust and sets realistic expectations. For added peace of mind, consider offering shipment insurance and guaranteed delivery dates for distant locations.
Navexa simplifies these logistics with features like multi-carrier rate comparisons, inventory forecasting, and automated order routing. These tools help e-commerce businesses trim shipping costs by 10–15% while ensuring quicker, more dependable deliveries.
How do shipping zones influence fulfillment costs for e-commerce businesses?
Shipping zones are geographic areas that carriers use to figure out how far a package needs to travel. In the U.S., these zones are typically numbered from 1 to 8 for domestic shipments. The closer the zone (like Zone 1, which represents the origin ZIP code), the cheaper and faster the shipping. On the flip side, higher zones mean greater distances, which translate to higher costs and longer delivery times.
For e-commerce businesses, knowing how shipping zones work is key to improving fulfillment strategies. By storing inventory in multiple locations closer to areas with high demand, businesses can keep shipments within lower-cost zones. This approach not only cuts down on shipping expenses but also helps meet the growing customer demand for faster delivery. Additionally, understanding zones allows businesses to make smarter choices when it comes to selecting carriers, comparing rates, and deciding on packaging.
Navexa offers tools designed to make this process easier. Features like multi-carrier rate shopping, intelligent box optimization, and inventory forecasting can help businesses lower shipping costs by 10-15%. At the same time, these tools ensure operations stay efficient without compromising delivery speed or service quality.
Ready to optimize your fulfillment?
Start saving on shipping costs and streamline your operations with Navexa.
